Software Architecture¶
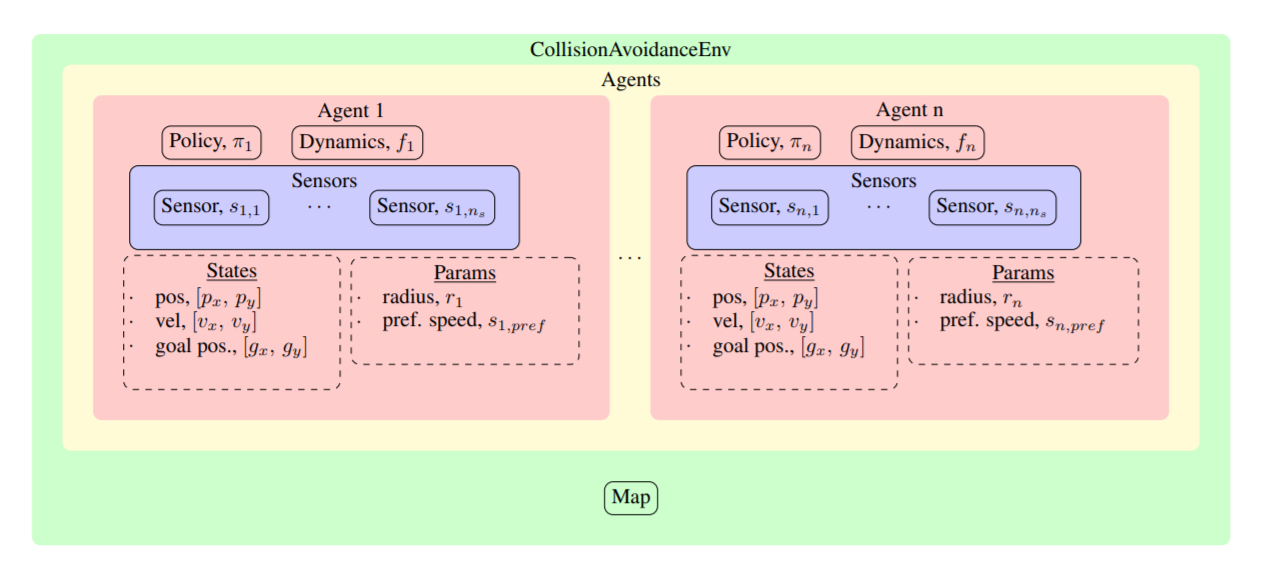
There are 5 key types of objects: CollisionAvoidanceEnv, Agent, Sensor, Policy, and Dynamics.
A simulation begins by creating an instance of the CollisionAvoidanceEnv : env = CollisionAvoidanceEnv()
After initialization, the CollisionAvoidanceEnv contains a list of Agent s, stored at env.agents (More on how this list gets populated, later).
Each Agent in that list has a Policy, Dynamics, a list of Sensor s, and other attributes about its state, such as its current position, velocity, radius, and goal position.
An external process moves the CollisionAvoidanceEnv forward in time by calling env.step, which triggers each Agent to:
- use its
Policyto compute its next action from its current observation - use its
Dynamicsmodel to compute its next state by applying the computed action - use its
Sensors to compute its next observation by measuring properties of theCollisionAvoidanceEnv.
The env.step call returns useful information to the caller (not in this order):
- next_obs: All agents’ next observations, computed by their Sensors, are stuffed into one data structure. Note: This is only useful if some
Agents have ExternalPolicies, otherwise theCollisionAvoidanceEnvalready has access to the eachAgent’s most recent observation and does action selection internally. - info: The
CollisionAvoidanceEnvwill also check whether anyAgents have collided with one another or a static obstacle, reached their goal, or run out of time. If any of these conditions are True, thatAgentis “done”, and a dict of which agents are done/not is put into info. - game_over: If all agents are “done”, then that episode is “done”, which is also returned by the env.step call (“game_over”) [Note: the condition on when to end the episode, (e.g., wait for all agents to be done, just one, just ones with certain properties) can be adjusted]
- reward: In the process of checking for collisions and goal-reaching, the
CollisionAvoidanceEnvalso computes a scalar reward for eachAgent; the reward list is returned by the env.step call